TECHNOLOGY
The tech behind KETEK
TECHNOLOGY
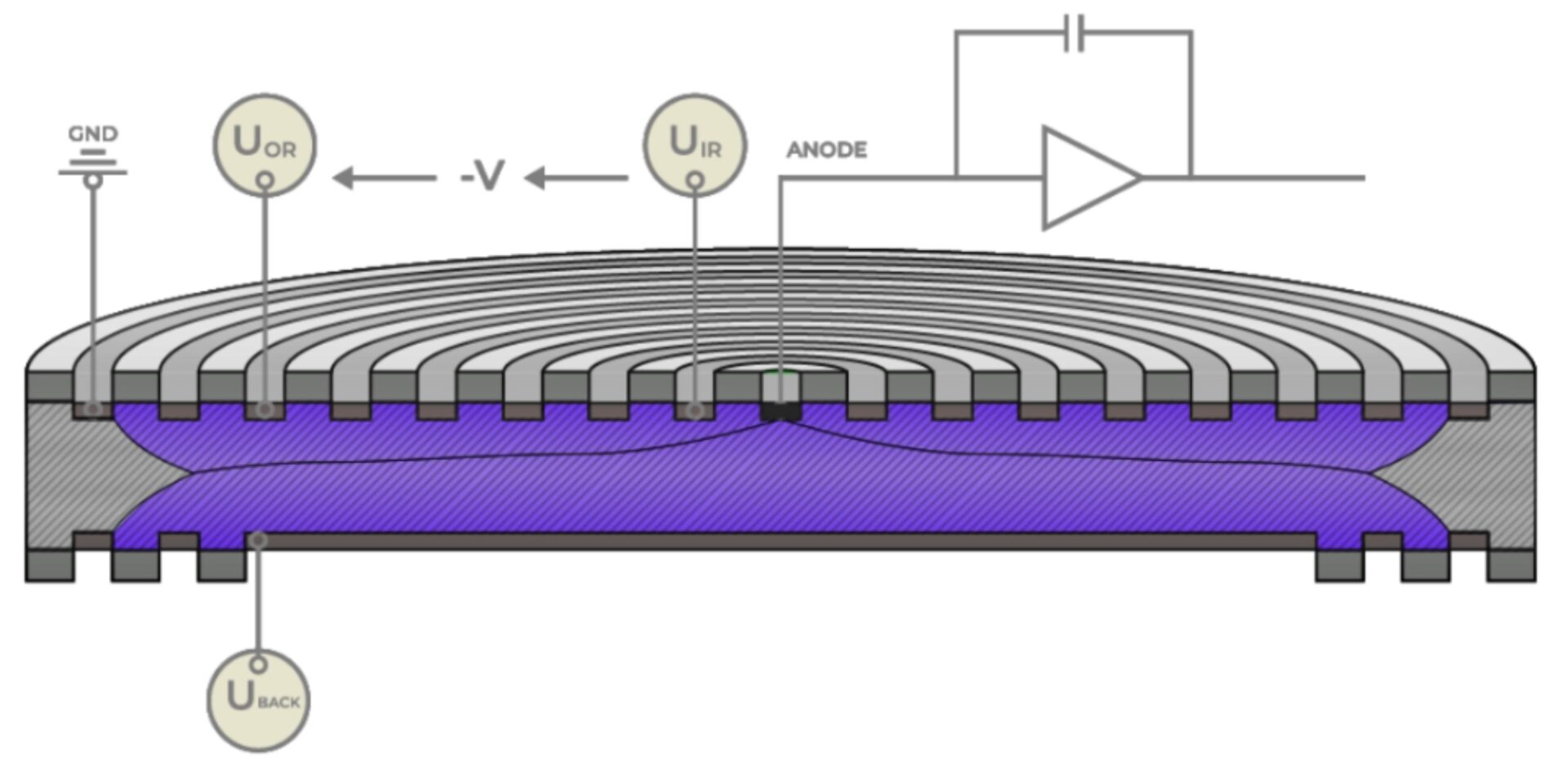
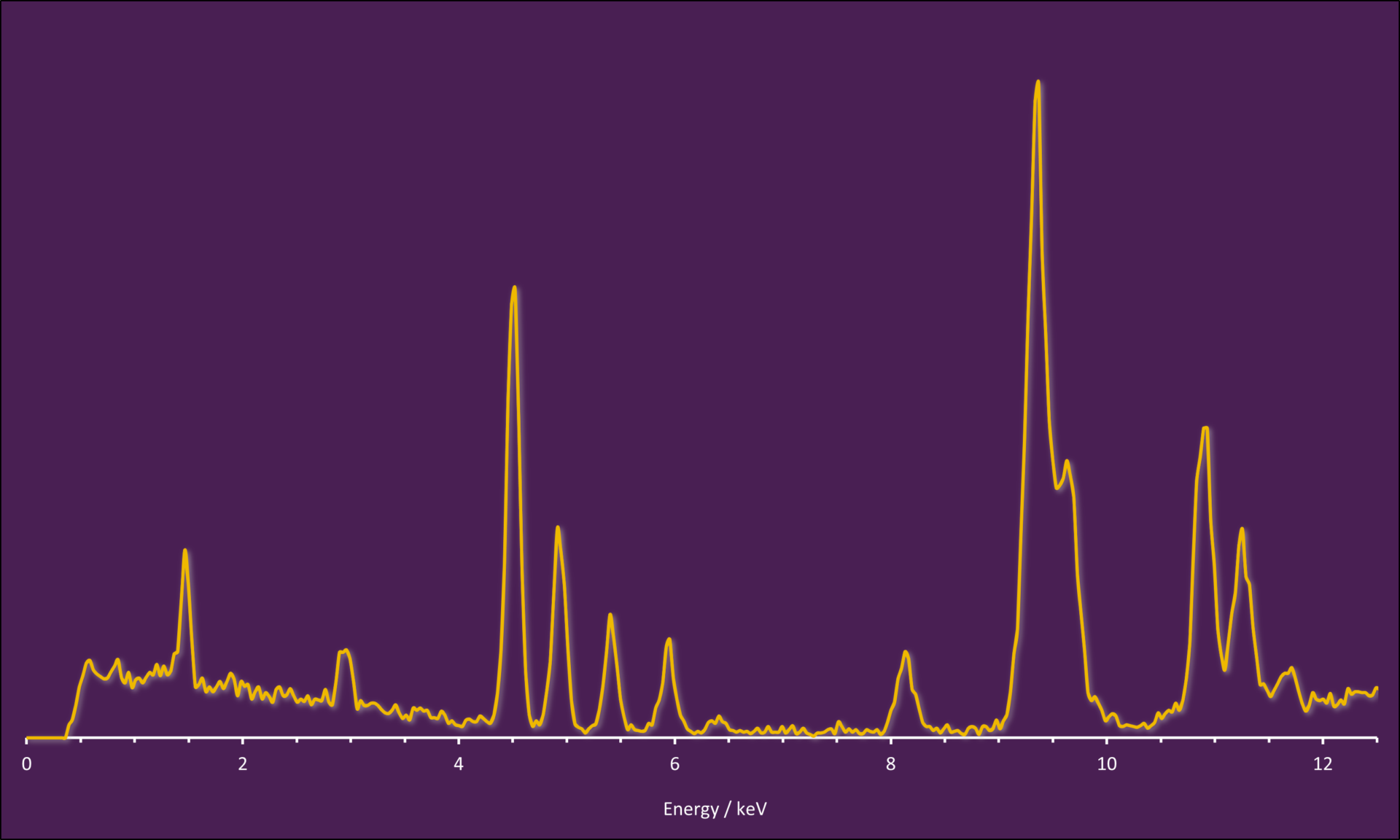
The Silicon Drift Detector (SDD) is a semiconductor sensor designed for precise and accurate energy measurements of soft and medium-hard X-ray radiation. It is widely used in material analysis applications, where determining the elemental composition of a sample is essential. The SDD facilitates the detection of nearly all elements in the periodic table, starting from lithium, making it an indispensable tool in techniques such as X-ray fluorescence (XRF) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX).
Key advantages of KETEK SDDs include their compact design, outstanding X-ray photon energy resolution, high count rate capability, and excellent sensitivity to radiation emitted by all characteristic X-ray-emitting elements.
These advantages require a deep understanding of several key technologies: enhanced semiconductor processing, optimized SDD chip design, e.g. realization of an ultra-low capacitance electrode, sub-freezing cooling technology, and KETEK’s highly specialized, ultra-fast, low-noise signal processing electronics.
The three subsections SDD Cross Section, Working Principle and Signal Processing provide more detailed information on how an SDD module is constructed, how X-rays can be detected by an SDD chip and the path from the detection of individual X-rays to a complete energy-dispersive spectrum.